A lien is a legal claim that protects the lender until a debt is paid.
Can You Put a Lien on a Car as an Individual?
Yes, you can. You don’t need to be a bank or finance company. If you sold a car with payments or loaned someone money to buy a vehicle, you can list your name as the lienholder.
Adding a lien protects you. If the buyer stops paying, it gives you legal right to take the car back. Before you put your name on the title, it’s smart to check if a lien already exists since most states allow only one lienholder at a time.
This guide shows you who qualifies, how to file, and what paperwork you’ll need to put a legal lien on a car title.
Key Takeaways
- To add a lien, bring the vehicle title and a completed application to your local DMV or tax collector’s office.
- Lenders, private sellers financing a sale, mechanics owed for repairs, and courts can all file liens.
- If you’re selling a car with payments, you’re acting as the lender and can list yourself as lienholder for protection.
- The lien stays on the title until the debt is paid in full and the lienholder files a release.
- Title fees range from $18 to $85 depending on your state, and processing takes about 7 to 14 business days.
Who Can Put a Lien on a Car Title
Not everyone can place a lien on a vehicle. You can only file if someone owes you money related to the car. Here’s who qualifies and why.
Finance Lien
Banks and credit unions place liens when they finance a car purchase. The lien protects their investment by giving them the right to repossess the vehicle if the borrower stops making payments.
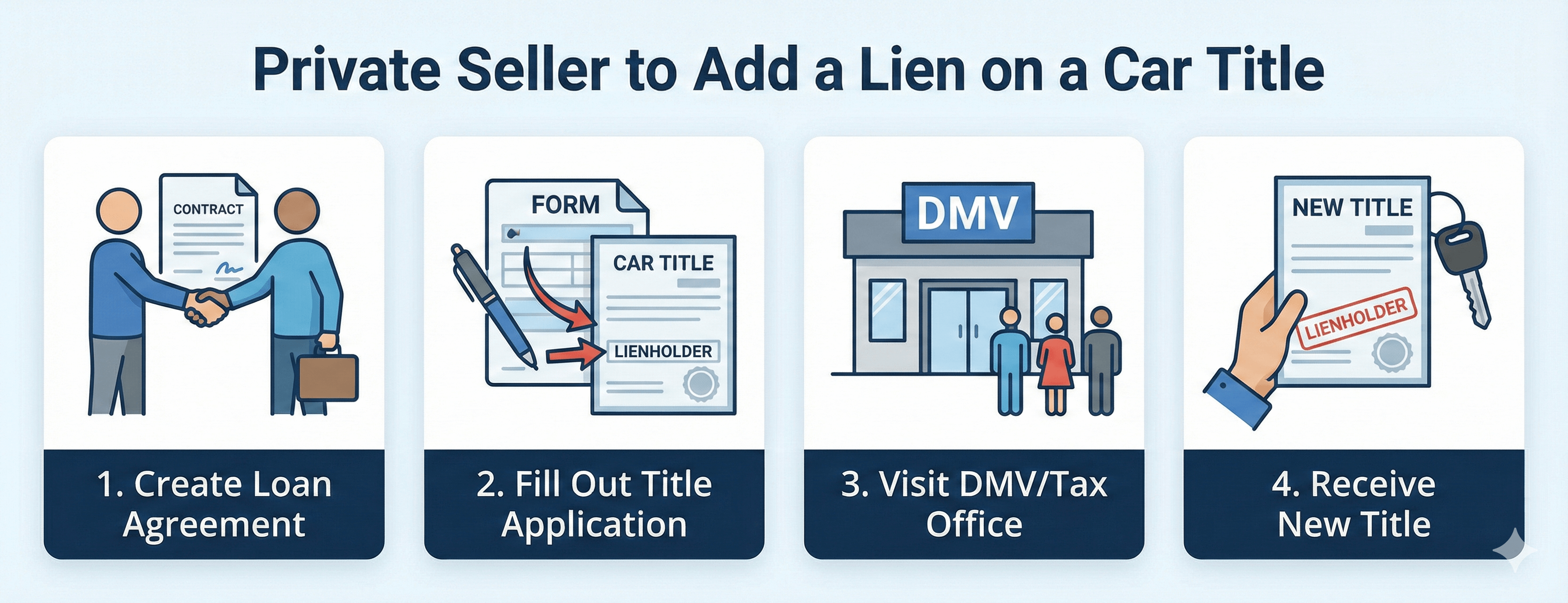
Private Seller Lien
If you sell your car to someone and let them pay over time, you can file as the lienholder. This works the same way as a bank loan. You hold the title until they pay in full, and if they stop paying, you have legal right to take the car back.
Mechanic’s Lien
Auto repair shops can file a lien if a customer doesn’t pay for completed work. This lets them hold onto the vehicle or eventually sell it to recover the money owed.
Most states require shops to send written notice before filing, but sometimes this happens without the owner knowing until they try to sell or refinance.
Judgment Lien
Courts can grant creditors the right to place a lien after winning a lawsuit. Child support agencies also use this method when a parent falls behind on payments.
Tax Lien
Federal, state, and local tax authorities place liens when taxpayers don’t pay what they owe. Tax liens usually take priority over other claims and must be cleared before the vehicle can be sold.
How to Add a Lienholder to a Car Title
The exact process depends on your state, but the steps are similar everywhere. Here’s what to expect.
Visit Your DMV or Tax Collector
Go to your local DMV or county tax collector’s office with the original vehicle title. If you don’t have it, you may need to apply for a duplicate first.
Fill Out the Application
Complete the title application form with details about the vehicle and both parties. You’ll typically need:
- Vehicle year, make, model, and VIN
- Current owner’s name and address
- New lienholder’s name and address
- Signatures from both the owner and lienholder
Pay the Fee and Submit
Hand in your completed application along with the original title and pay the fee. You’ll get a receipt showing the transaction was processed.
Wait for the Updated Title
Processing usually takes 7 to 14 business days. The new title showing the lienholder will be mailed to the lienholder’s address, or you may receive digital confirmation if your state uses electronic titles.
Can You Put a Lien on a Car Title Online?
Yes, but it depends on who you are. Banks and finance companies usually handle lien filing digitally through the state’s DMV or titling system.
For private loans or individuals not connected to these systems, you’ll need to download specific forms, fill them out, and submit them to the DMV either electronically through a portal or by mail.
How to File a Lien Online (If Available in Your State)
Check If Your State Offers Online Filing
Visit your state’s DMV website and search for “add lienholder” or “electronic lien and title.” Most states have Electronic Lien and Title (ELT) systems, but these are typically for licensed lenders only.
Download the Required Forms
Even for online submissions, you’ll need a title amendment or application form. Fill it out with the vehicle info, owner info, and lienholder details.
Submit Through the State Portal or by Mail
Some states let you upload documents through their DMV portal. Others require you to mail the completed forms with payment.
Receive the New Title
Once processed, you’ll get an updated title reflecting the lien. Electronic titles update within 1 to 2 business days. Paper titles take 7 to 14 business days by mail.
Timeline: How Fast Can It Be Done?
- Banks and licensed lenders (ELT system): 1 to 2 business days
- Dealers using state portals: 1 to 2 business days
- Individuals filing by mail: 7 to 14 business days
- In-person at DMV or tax office: Same day to 7 business days
Important: Each state has its own process, forms, and fees. The steps above are general guidelines. Check your state’s DMV website for exact requirements, or see the state-by-state section below for specific details.

Protecting Yourself When Selling a Car With Payments
Selling a car with a payment plan puts you at risk. If the buyer stops paying, you could lose both the car and the money they still owe you.
Adding yourself as lienholder on the title gives you protection. The buyer can drive the car, but they can’t sell or refinance it without your permission. If they stop paying, you have legal claim to the vehicle.
Here’s How to Set It Up:
- Write a loan agreement that includes the sale price, payment schedule, and what happens if payments stop
- Have both parties sign the agreement and keep copies
- Visit the DMV together to transfer the title with you listed as lienholder
State-by-State Information
Each state has its own forms, fees, and procedures. Here’s what you need to know for four common states. Always check with your local office for current requirements.
California
Use Form REG 343 (Application for Title or Registration) and submit it with the original title at any DMV office. The fee is $23 and processing takes about two weeks. For questions, call (800) 777-0133.
Online option: Banks and finance companies must use California’s Electronic Lien and Title (ELT) system, which processes in 1 to 2 days. Private individuals cannot file online and must visit a DMV office or mail the forms.
Texas
Use Form 130-U to add a lienholder, or Form VTR-267 if there’s already a lien on the title. Submit to your county tax assessor-collector. Fees run $28 to $33. For questions, call (888) 368-4689.
Online option: Licensed dealers can use the webDEALER system to file electronically. Lenders use the Texas ELT program. Private individuals must visit the county tax office in person.
Georgia
Use Form MV-1 (Motor Vehicle Title Application) at your county tag office. The fee is $18. For questions, call (855) 406-5221.
Online option: Georgia has an ELT program for lenders. Private individuals must visit a county tag office in person to add a lien.
Florida
Use Form HSMV 82040 (Application for Certificate of Title) at your county tax collector’s office. The fee is about $78 including the lien recording fee. For questions, call (850) 617-2000.
Online option: Florida requires all lenders to use the Electronic Lien and Title (ELT) system. Private individuals can submit forms by mail or visit a tax collector’s office. You can check title status through the MyDMV Portal at flhsmv.gov.
Can Anyone Put a Lien on a Car?
No, you need a legitimate financial or legal claim. This includes lenders who financed the vehicle, mechanics owed for repairs, creditors with court judgments, and government agencies collecting unpaid taxes.
You can’t place a lien just because someone owes you money from an unrelated matter.
How Long Does a Lien Stay on a Title?
A lien stays on the title until the debt is paid in full and the lienholder files a release. There’s no automatic expiration, so even if payments stop, the lien remains attached to the vehicle.
Can a Mechanic Put a Lien on My Car Without My Permission?
In most states, yes. If you authorized the repairs but didn’t pay for them, the shop can file a mechanic’s lien. They don’t need your consent, though they usually must follow specific procedures like sending written notice first.
What Happens After I Add a Lienholder?
The lienholder’s name appears on the title. The owner keeps the car and can drive it normally, but they cannot sell or transfer the vehicle without the lienholder signing off to release the lien.
How Do I Remove a Lien After the Debt Is Paid?
Once the debt is paid, the lienholder provides a lien release document. You submit this to your DMV to get a clear title. For detailed steps, see our guide on how to remove a lien from a car title.
What’s the Difference Between a Car Lien and a Car Loan?
A car loan is the money you borrow to buy the vehicle. A lien is the legal claim that protects the lender until you pay it back. Think of it this way: the loan is the debt you owe, and the lien is the security that guarantees it.
Can You Put a Lien on a Car Without the Title?
No. You need the original title to add a lienholder. If the title is lost, you must apply for a duplicate title first through your state’s DMV before you can add a lien.
Will a Car Lien Affect My Insurance?
Yes. Most lienholders require you to carry full coverage insurance (comprehensive and collision) until the loan is paid off. This protects their investment if the car is damaged or stolen. Once you pay off the lien, you can reduce your coverage.
Can a Car Lien Hurt My Credit?
It depends on the type. A regular car loan (consensual lien) won’t hurt your credit as long as you make payments on time. But mechanic’s liens and judgment liens from unpaid debts can stay on your credit report for up to 7 years and lower your score.
Bottom Line
Adding a lien to a car title is straightforward. Visit your local DMV or tax collector’s office, fill out the paperwork, pay a small fee, and wait for the updated title.
The lien stays on the title until the debt is paid, so you’re protected if payments stop. For more about how liens work, see our complete guide on what a lien on a car title means.
Still Have Questions About Vehicle Liens?
Our team can help you!
Related Resources